Presented at AlYamamah Hospital on 25th July 2021. By: Professor Omar Hasan Kasule Sr. MB ChB (MUK), MPH (Harvard), DrPH (Harvard) Professor of Epidemiology and Bioethics, King Fahad Medical City R2 Cluster
OBJECTIVES:
► Hospital, the trial site: PI, sub-investigators, research assistants/coordinators, technicians, technicians.
► Participants: patients and healthy volunteers.
► Institutional review board (IRB): internal approval.
► Saudi Food and Drug Authority: external approval and monitoring.
► Sponsor and/or Contract Research Organization (CRO).
KEY
STAKEHOLDERS:
► Hospital, the trial site: PI, sub-investigators, research assistants/coordinators, technicians, technicians.
► Participants: patients and healthy volunteers.
► Institutional review board (IRB): internal approval.
► Saudi Food and Drug Authority: external approval and monitoring.
► Sponsor and/or Contract Research Organization (CRO).
THE
PROTOCOL - 1: Describes the conduct of the trial:
- Protocol
title, protocol number, protocol date, and protocol version (very
important).
- Names
and addresses of the sponsor, the principal investigator, the laboratory
to be used,
- Protocol
synopsis,
- Background
including the rationale, the population, risks, and benefits
- Trial
objectives/outcomes (primary and secondary),
- Trial
design such as double-blind, placebo-controlled, open-label, etc. A flow
diagram is recommended for clarity, study population, details of
randomization, eligibility criteria (inclusion and exclusion)
THE
PROTOCOL - 2:
- Construct
a research protocol and accompanying documents for obtaining regulatory
approval.
- Assemble
resources needed for a clinical trial: budget, personnel, materials, and medications.
- Organize
the enrollment, randomization, medication, and data collection.
- Conclude
the study with close-out, final report, and publication of the results.
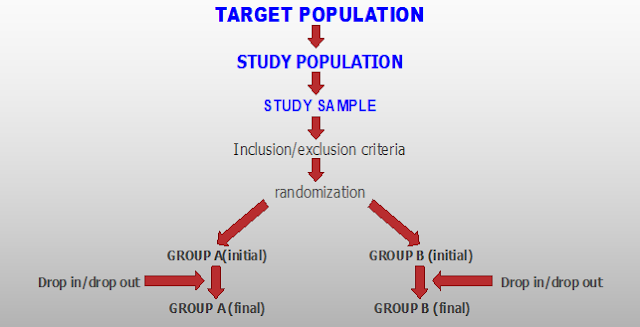
FIGURE:
INFORMED
CONSENT:
- Informed
consent according to GCP guidelines.
- Process
of full information disclosure: make sure participant understands
procedures, risks, benefits, and agrees voluntarily and that they can
withdraw without giving a reason.
- Signing
and dating the informed consent document.
- Reconsenting
in case of change of any information disclosed especially protocol
amendments and adverse events.
INVESTIGATOR
BROCHURE:
- Provides
summary information about the investigational product for the benefit of
the investigator and regulatory authorities.
- The sponsor prepares and updates the investigator brochure.
- Properties
of the investigational product: physical, chemical, pharmacological.
- Details
of the drug: doses and frequency, routes of administration.
- Previous
studies on the IP: in vitro, in vivo, animal, and human.
- Summary
and guidance for the investigator.
REQUIREMENTS
AT THE SITE:
- Investigational
drug room in the pharmacy to store and dispense study drugs.
- Laboratory
and other facilities for collecting, analyzing specimens or shipping the
for analysis elsewhere.
- Wards,
outpatient facilities, examination rooms.
- Offices
for research personnel and record storage.
- Research
staff: PI, sub-investigators, research coordinators, statisticians,
pharmacists.
- Satisfactory
site visit report.
APPROVALS:
- Regulatory
approval by IRB. Submission of the protocol, investigator brochure,
informed consent forms, case record form (CRF), CVs and GCP certificates
of principal researchers, insurance, and contracts (as needed).
- Regulatory
approval by SFDA: Same submissions as IRB either simultaneously or SFDA
after IRB. After SFDA approval the study is registered in the clinical
trials register.
- Export
license for specimens being sent overseas for analysis. Material Transfer
Agreement (MTA) and Data Transfer Agreement (DTA) may be needed.
- Approval
by the head of the department where the study will be carried out.
CLINICAL
TRIAL AGREEMENT (CTA):
► CTA is signed between the sponsor and the hospital. It covers technical and financial matters. The technical matters must conform to the GCP principles.
► The following are included: timelines, confidentiality, intellectual property, indemnity insurance and compensation, how to terminate.
► Details of payments to the hospital and the research staff are also specified.
PLANNING:
- Make a
list of all events in the form of a calendar and have a pre-trial checklist.
- Construct
a trial budget with a detailed costing of costs of study personnel,
consumables, site costs, pharmacy, laboratory, training, and management.
- Prepare
a staff work schedule.
- List all
equipment and supplies needed and plan restocking.
RESEARCH
STAFF TRAINING:
- Internal
training
· Orientation program for all new staff
· Training on standard operating procedures
· Health and safety training
- External
training
· Investigator meeting to train investigators on this
study
· Site initiation meeting to go over all trial
procedures and documents
· GCP training
PATIENT
RECRUITMENT:
- Motivations:
medical care, service to society, remuneration? Sensitive.
- How will
you access the target population, participant commitment, perceptions,
and literacy?
- Recruitment
options: hospitals and health centers, referrals, databases, patient
support groups, community groups, and advertising.
- Attrition
of participants why?
INVESTIGATIONAL
PRODUCT MANAGEMENT:
- Importation,
storage, and logging.
- Environmental
conditions: temperature, humidity, light.
- Randomization,
blinding, and dispensing.
- Study
close-out and IP destruction.
- IP
accountability.
STUDY
CONDUCT:
- Screening
period
· Recruit and pre-screen,
· Informed consent,
· Protocol specific screening
- Treatment
Period
· Confirm eligibility (inclusion/exclusion.
· Perform protocol procedures.
· Perform quality checks (QC and QA).
- Safety
follow up
· End visit follow up
SPECIMENS
(blood, urine, etc.) COLLECTION, PROCESSING, SHIPMENT, etc.:
- Techniques
of collection and laboratory processing.
- Shipment
overseas.
STUDY
DOCUMENTS (paper or electronic):
- Source
data is data in original records or certified copies. ALCOA = Attributable,
Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate.
- Source
documents and responsibilities of the Sponsor or PI.
DATA
MANAGEMENT:
- Establish
and train on quality standards.
- Database
designing, building, testing, and implementing, CRF is a key document.
- Database
lock: record locking, record signing off.
- Data
export for analysis.
- Archiving,
sharing, and publishing.
MONITORING,
AUDITING, and INSPECTION:
- The sponsor is responsible to monitor to ensure that the trial follows GCP.
- Monitoring
checks on the safety and well-being of participants, accuracy, and completeness
of the data.
- Records
of the monitoring visit are kept and the PI and Sponsor are informed.
- Auditing.
- Inspection.
SUMMARY
OF STEP - 1:
- Define
the problem of the research and the hypotheses. Write a synopsis. Type of
study phase 1-4?
- Find a
sponsor: trials are expensive and need a lot of money.
- Select
the site: assess its suitability and feasibility.
- Finalize
study documents: protocol, investigator brochure, and informed consent
documents.
- Submit
to IRB for internal approval.
- Finalize
contracts with researchers, sponsors, and the hospital.
- Submit
to SFDA for external approval.
SUMMARY
OF STEP - 2:
- Recruit
PI, sub-investigators, and other study personnel.
- Obtain
IRB and SFDA approval.
- Site
initiation meeting.
- Staff
training.
- Receive
the investigational product.
- Conduct
the study.
- Database
lock.
- Close out,
archive, destroy extra IP, publish results, and submit to SFDA for drug
registration.