Presented at CRC course KFMC on January 26, 2020 11-12am by Prof Omar Hasan Kasule Sr Professor of Epidemiology and Bioethics, King Fahad Medical City.
CHARACTERISTICS OF EPIDEMIOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION
• Epidemiological methodology follows the scientific method
• Epidemiological investigation is not as deterministic as laboratory investigation but is cheap and easy.
• Epidemiology is empirical: epidemiology relies on and respects only empirical findings. Empiricism refers to reliance on physical proof.
• Epidemiology is inductive: induction is building a theory on several individual observations.
• Refutative: refutation is basically refusal of a supposition until it is proved otherwise.
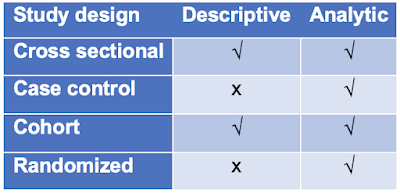
DESCRIPTIVE AND ANALYTIC STUDY DESIGNS
DATA ANALYSIS
• Data summarization,
• Estimation
• Interpretation.
DATA VALIDATION
• Simple manual inspection of the data is needed before statistical procedures.
• Preliminary examination consists of looking at tables and graphics.
• Descriptive statistics are used to detect errors, ascertain the normality of the data, and know the size of cells.
• Missing values may be imputed or incomplete observations may be eliminated.
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
• Mean and standard deviation
• Proportion (prevalence and variance)
ANALYTIC STATISTICS: ASSOCIATION
• T student statistic
• chi-square statistic
• linear correlation,
• regression coefficients.
ANALYTIC STATISTICS: EFFECT
• Odds Ratio
• Risk Ratio
• Rate difference.